Circuit Training
Circuit Training
Introduction
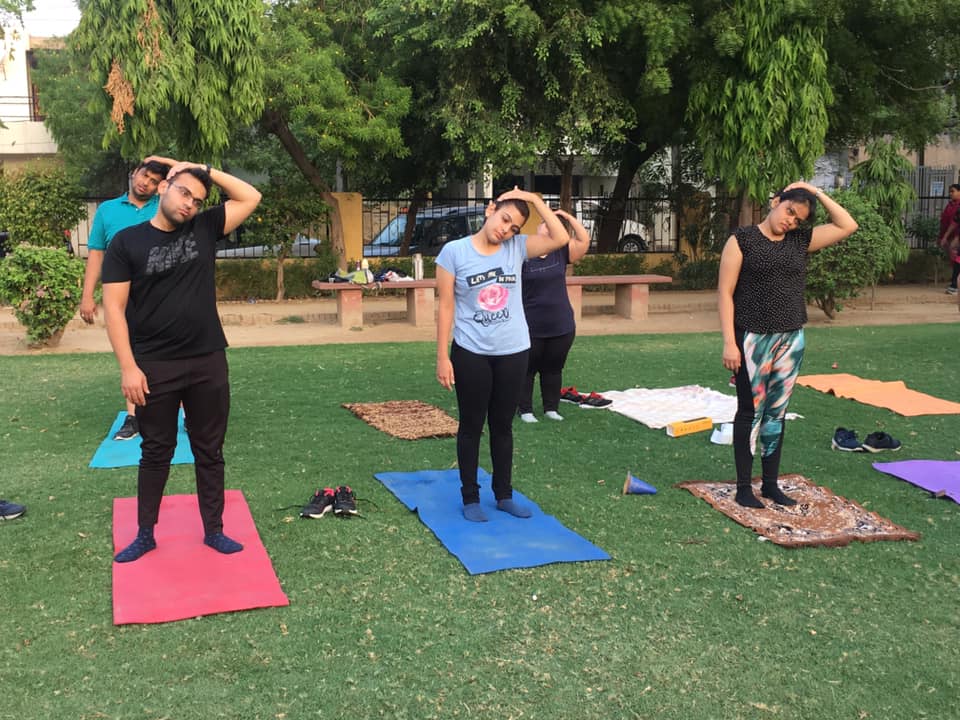
A set of exercises are performed in succession with little rest in between as part of the time- and energy-saving Circuit Training technique. It targets various muscle areas, boosts general fitness, and provides a full-body workout by combining cardiovascular and strength workouts. The following information regarding circuit training:
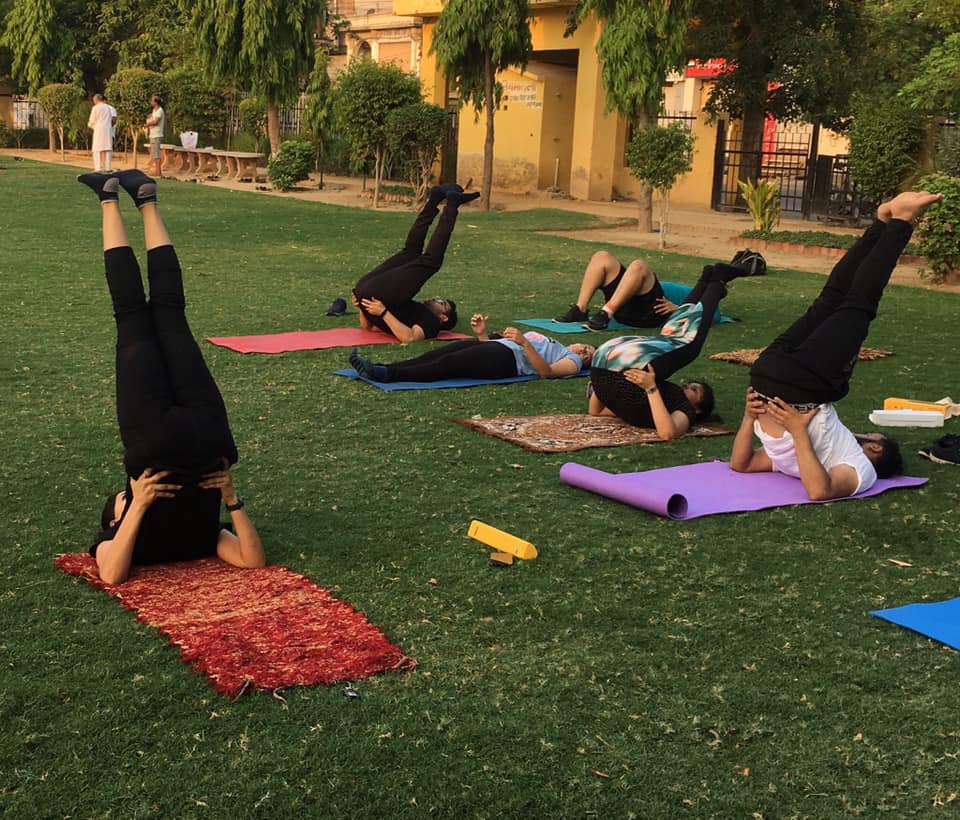
How Circuit Training Works: In circuit training, you move through the exercise stations in a specific order. Each training station concentrates on a particular muscle group or aspect of fitness. To give a well-rounded workout, the circuit usually consists of a combination of cardiovascular activities (such as jumping jacks and high knees) and strength exercises (such as push-ups and squats).
Benefits of Circuit Training:
Time-Effective: Circuit training minimizes the amount of time required to complete a thorough workout by combining both aerobic and strength workouts in a single session.
Full-Body Workout:
It uses a variety of muscle groups, fostering the development of balanced strength and enhancing total muscular endurance.
Cardiovascular Endurance: By alternating between activities, the heart rate is raised, which enhances cardiovascular fitness and burns calories.
Flexibility: Circuit training is adaptable to a range of fitness levels and objectives. Beginner, intermediate, and experienced participants can all benefit from different exercises and levels of difficulty.
Exercise that effectively burns fat is circuit training because it combines cardio and strength training.
Circuit training is suitable for home workouts or locations with few resources because it requires little in the way of equipment.
Design a Circuit:
Identify Exercises:
Choose a variety of exercises that target different muscle groups and involve both cardiovascular and strength components.
Determine Work and Rest Intervals: Decide on the duration for each exercise (e.g., 30 seconds) and the rest time between exercises (e.g., 10 seconds).
Set the Circuit Length: Determine the number of exercise stations in the circuit (e.g., 8-10 stations) based on available time and fitness level.
Customize for Participants: Tailor the circuit to match the participants’ fitness levels, incorporating progressions or regressions as needed.
Sample Circuit Training Routine:
Bodyweight Squats: 30 seconds
Push-Ups: 30 seconds
Mountain Climbers: 30 seconds
Lunges: 30 seconds (alternating legs)
Tricep Dips: 30 seconds
High Knees: 30 seconds
Plank Hold: 30 seconds
Rest: 10 seconds between exercises
Complete the circuit 2-3 times, with a 1-2 minute rest between circuits.